Acid base titration curve pdf unveils the secrets and techniques of acid-base reactions, providing a visible roadmap by the fascinating world of chemistry. This complete information explores the basic ideas, sensible methods, and real-world functions of acid-base titrations. From understanding the essential position of indicators to mastering the artwork of correct measurements, the curve reveals a wealth of details about the options it examines.
Get able to embark on a journey of discovery, unraveling the mysteries hidden inside these intricate chemical processes.
This information walks you thru the method of developing, decoding, and making use of titration curves. It particulars the meticulous steps concerned, together with calculating pH values, getting ready customary options, and figuring out equivalence factors. The doc additional delves into troubleshooting frequent errors and affords precious insights into the varied functions of acid-base titrations throughout varied scientific disciplines.
Introduction to Acid-Base Titration Curves: Acid Base Titration Curve Pdf
Acid-base titrations are basic experiments in chemistry, permitting us to exactly decide the focus of an unknown acid or base. Think about making an attempt to determine the precise energy of a cleansing answer—a titration helps us quantify that energy. This course of is essential for understanding chemical reactions and their quantitative features. It’s like discovering the right steadiness in a recipe, making certain the correct amount of every ingredient.The elemental precept behind acid-base reactions lies within the switch of protons (H+ ions).
Sturdy acids readily donate protons, whereas sturdy bases readily settle for them. The response is actually a neutralization course of, the place the acid and base react to type water and a salt. This course of is very predictable and quantifiable, making it helpful for varied functions, from laboratory evaluation to industrial processes. Titration curves visually symbolize the change in pH as a base is added to an acid, or vice versa.
Basic Rules of Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions contain the switch of protons (H+ ions). Sturdy acids fully dissociate in water, releasing all their protons. Weak acids solely partially dissociate. Equally, sturdy bases fully ionize in water, releasing hydroxide ions (OH-), whereas weak bases solely partially ionize. The energy of an acid or base dictates how readily it donates or accepts protons, respectively.
Understanding these ideas is significant to decoding titration curves.
Elements of a Typical Acid-Base Titration Setup
A typical acid-base titration setup entails a number of key parts. These parts work collectively to permit for correct measurement and evaluation of the response. This precision is essential for figuring out the focus of the unknown answer.
| Part | Description | Perform |
|---|---|---|
| Burette | A graduated glass tube with a stopcock. | Used to exactly ship a recognized quantity of titrant (the answer of recognized focus). |
| Erlenmeyer Flask | A conical flask used to carry the analyte (the answer with unknown focus). | Accommodates the answer being analyzed. |
| Indicator | A substance that adjustments coloration at a selected pH vary. | Alerts the endpoint of the titration by altering coloration. |
| Stand | A sturdy help for the burette | Maintains the steadiness of the burette. |
Position of Indicators in Acid-Base Titrations
Indicators are substances that exhibit distinct coloration adjustments at particular pH values. These coloration adjustments mark the endpoint of the titration, which is the purpose the place the response is full. Selecting the suitable indicator is essential, as the colour change should happen near the equivalence level (the purpose the place the moles of acid and base are stoichiometrically equal).
Totally different indicators have totally different coloration adjustments at totally different pH ranges, permitting for several types of titrations. For instance, phenolphthalein adjustments coloration in a barely primary vary, whereas methyl orange adjustments coloration in a extra acidic vary. This enables chemists to pick an indicator that precisely displays the response’s endpoint.
Developing Acid-Base Titration Curves
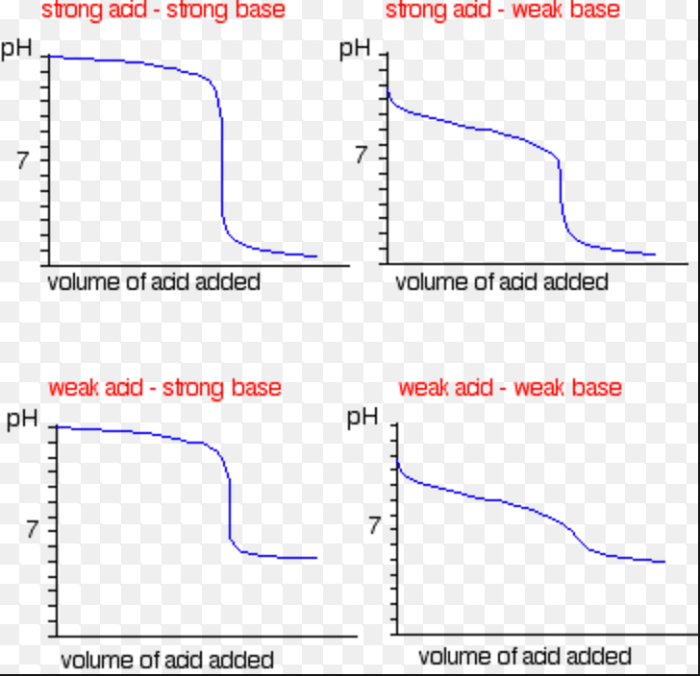
Unveiling the secrets and techniques of acid-base reactions typically entails meticulously charting their progress. A titration curve, a graphical illustration of pH adjustments throughout a titration, offers invaluable insights into the character of the response. It is a roadmap to understanding the energy of acids and bases and the equilibrium dynamics at play.Plotting a titration curve entails a collection of cautious steps, from exactly measuring volumes to calculating pH values.
Correct measurements are paramount, as small errors can result in vital deviations within the curve’s form. Understanding these steps and the calculations behind them empowers us to interpret the information successfully and draw significant conclusions.
Steps Concerned in Plotting a Titration Curve
This part particulars the essential steps concerned in making a titration curve, a visible illustration of the acid-base response’s development. Cautious consideration to element is crucial for dependable outcomes.
- Put together an answer of recognized focus (the titrant) and measure a exact quantity of the unknown answer (the analyte). The titrant is added incrementally to the analyte.
- Measure the pH of the answer after every addition of titrant. Use a pH meter or indicator answer for correct pH willpower.
- Plot the pH values towards the quantity of titrant added. This generates the titration curve.
Calculating pH Values
Correct pH calculations are important for precisely decoding the titration curve. The tactic employed is dependent upon the stage of the titration.
- Earlier than the equivalence level, the pH is primarily decided by the focus of the analyte. Calculations involving the preliminary focus and the quantity of titrant added are essential.
- On the equivalence level, the moles of acid and base are equal. The pH at this level is dependent upon the character of the acid and base. Calculations typically contain the usage of the Ka or Kb values.
- Past the equivalence level, the pH is primarily decided by the surplus titrant. Calculations utilizing the focus and quantity of the surplus titrant are needed.
Significance of Correct Measurements
Exact measurements are very important for correct leads to any titration experiment. This precision ensures the reliability of the titration curve and the conclusions drawn from it.
- Exact quantity measurements are essential. Use calibrated glassware like burets and pipettes to reduce errors.
- Correct focus of the titrant is crucial. Standardization procedures are important to make sure accuracy.
- Common calibration of the pH meter ensures correct pH readings.
Making ready a Standardized Answer
A standardized answer is one whose focus is exactly recognized. That is essential for correct titrations.
- Weighing: Precisely weigh a exact quantity of major customary (a substance with excessive purity and recognized stoichiometry) utilizing an analytical steadiness.
- Dissolving: Dissolve the weighed major customary in a recognized quantity of solvent, normally distilled water.
- Calculating: Calculate the focus of the ensuing answer utilizing the components: Focus = (mass of solute / molar mass of solute) / quantity of answer.
Contrasting pH Modifications Throughout Titrations
The next desk summarizes the pH adjustments through the titration of varied acid-base combos.
| Acid/Base | pH Change | Equivalence Level |
|---|---|---|
| Sturdy Acid with Sturdy Base | Sharp enhance round equivalence level | Round pH 7 |
| Weak Acid with Sturdy Base | Gradual enhance round equivalence level | Above pH 7 |
| Weak Base with Sturdy Acid | Gradual lower round equivalence level | Under pH 7 |
Decoding Acid-Base Titration Curves
Unveiling the secrets and techniques hidden inside the elegant curves of acid-base titrations is like deciphering a hidden code. These curves, meticulously plotted, reveal important details about the response’s progress and the character of the interacting substances. They’re extra than simply fairly graphs; they’re highly effective instruments for understanding acid-base chemistry.The equivalence level, a pivotal second within the titration, signifies the exact stoichiometric steadiness between the acid and base.
It is like the last word handshake, the place the reactants have completely neutralized one another. The traits of the titration curves for sturdy and weak acids/bases fluctuate dramatically, mirroring the inherent variations of their chemical personalities. Realizing find out how to determine this significant equivalence level on a titration curve is paramount. The curves themselves act as silent storytellers, providing precious insights into the energy and nature of the reacting substances.
Evaluating and contrasting these curves is like evaluating the contrasting personalities of two buddies, revealing the underlying chemistry that drives their reactions.
Significance of Equivalence Factors, Acid base titration curve pdf
The equivalence level marks the stoichiometric level of the response. That is the place the moles of acid precisely equal the moles of base, leading to a impartial answer (pH = 7) for a robust acid/sturdy base response. For reactions involving a weak acid or base, the pH on the equivalence level will deviate from 7. Understanding this significant level is crucial for correct evaluation and figuring out the focus of unknown options.
Realizing the precise quantity of titrant wanted to succeed in the equivalence level permits for exact calculations.
Traits of Titration Curves for Sturdy and Weak Acids/Bases
Sturdy acids and bases fully dissociate in water, resulting in steep, vertical adjustments in pH close to the equivalence level. This abrupt shift is definitely noticed on the titration curve. Weak acids and bases, then again, solely partially dissociate, leading to a gentler, extra gradual change in pH close to the equivalence level. The form of the curve displays the equilibrium fixed for the dissociation of the weak acid or base.
Figuring out the Equivalence Level on a Titration Curve
The equivalence level is the purpose on the titration curve the place the steepest change in pH happens. It is the inflection level. Visualizing the curve helps. A pointy, sudden rise or fall in pH close to the equivalence level clearly signifies the response’s completion. This level on the graph permits for the exact willpower of the focus of the unknown answer.
Evaluating and Contrasting Titration Curves of Sturdy and Weak Acids
Sturdy acids exhibit sharp, vertical adjustments in pH close to the equivalence level, reflecting their full dissociation. Weak acids, in distinction, present a extra gradual shift in pH, indicating incomplete dissociation. This distinction within the curve’s form instantly corresponds to the inherent energy of the acid. The curves provide a visible illustration of the chemical nature of the reactants.
Abstract of Key Options of Titration Curves
| Sort of Acid/Base | Form of Curve Close to Equivalence Level | pH at Equivalence Level | Buffer Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sturdy Acid/Sturdy Base | Sharp, vertical change | 7 | Very small |
| Sturdy Acid/Weak Base | Sharp, vertical change | Lower than 7 | Small |
| Weak Acid/Sturdy Base | Gradual change | Better than 7 | Vital |
| Weak Acid/Weak Base | Gradual change | Variable (Is determined by the acid/base) | Vital |
Functions of Acid-Base Titration Curves
Acid-base titrations, a cornerstone of analytical chemistry, aren’t simply theoretical workout routines. They’re highly effective instruments with real-world functions, from figuring out the acidity of soil to making sure the standard of prescription drugs. Understanding how titration curves work unlocks the secrets and techniques hidden inside these chemical reactions.Titration curves present a visible roadmap of the response between an acid and a base. This roadmap reveals important details about the unknown answer, reminiscent of its focus and identification.
The form of the curve, notably the steep, vertical portion, affords clues to the character of the reactants concerned.
Figuring out the Focus of Unknown Options
Realizing the focus of an answer is essential in lots of fields. Titration curves provide a exact and dependable technique to find out unknown concentrations. By fastidiously measuring the quantity of a normal answer required to neutralize the unknown, the focus of the unknown answer might be calculated. This course of is crucial in industries like meals processing and environmental monitoring, the place correct measurements of acidity or alkalinity are important.
Figuring out Unknown Acids or Bases
The form of a titration curve is very depending on the character of the acid or base being titrated. Sturdy acids and bases yield distinctive curves in comparison with weak ones. The equivalence level, a pivotal level on the curve, may also help determine the unknown acid or base. The traits of the curve, together with the steepness and site of the equivalence level, present precious data to find out the identification of the unknown substance.
Actual-World Functions of Acid-Base Titrations
Acid-base titrations discover intensive functions in varied fields, demonstrating their broad utility. They’re indispensable in high quality management in pharmaceutical industries, making certain that medicines have the right energy and purity. Environmental scientists use titrations to watch the acidity of lakes and streams, making certain the well being of aquatic ecosystems. In meals science, titrations decide the acidity of fruit and veggies, which influences their style and preservation.
Situations The place Titration Curves Are Important
Titration curves are indispensable in quite a few situations. For instance, in a pharmaceutical lab, verifying the purity and focus of a drugs is paramount, the place titration curves are very important. Equally, figuring out the extent of acidity in industrial wastewater is essential to stop environmental harm, making titration curves important in environmental monitoring. Furthermore, in a chemistry lab, figuring out the kind of acid or base in an unknown answer depends on the distinctive options of the titration curve.
Desk of Functions in Totally different Fields
| Area | Software |
|---|---|
| Chemistry | Figuring out the focus of unknown acids and bases, figuring out unknown substances, and finding out acid-base reactions. |
| Environmental Science | Monitoring water high quality (acidity of lakes and streams), analyzing soil samples, and finding out air pollution ranges. |
| Meals Science | Figuring out the acidity of fruit and veggies, analyzing meals merchandise for correct preservation and style. |
| Medication | High quality management of medicines, making certain appropriate dosage and purity. |
Frequent Errors and Troubleshooting
Navigating the intricacies of acid-base titrations can generally really feel like a fragile dance. Understanding potential pitfalls and find out how to handle them is vital to attaining correct outcomes. This part will illuminate frequent errors, troubleshooting methods, and components affecting precision, empowering you to turn into a titration maestro.
Figuring out and Mitigating Errors
Errors in acid-base titrations can stem from varied sources, starting from imprecise measurements to flawed methods. Fastidiously contemplating these components is essential for dependable outcomes. Inaccurate preliminary readings, defective tools, and even environmental fluctuations can all affect the result. Addressing these points systematically will considerably enhance the accuracy and reliability of your titration experiments.
Imprecision in Measurement
Correct measurements are the cornerstone of exact titrations. Errors in measuring reagents, notably the titrant, can considerably skew the outcomes. Utilizing calibrated glassware, making certain correct approach, and minimizing parallax errors are important. A poorly calibrated buret, for instance, can result in inaccurate quantity readings, leading to an incorrect equivalence level willpower.
Troubleshooting Frequent Issues
Generally, regardless of meticulous preparation, sudden points can come up throughout a titration. Understanding the causes and treatments for these issues is significant. For example, if the answer’s coloration change is sluggish or erratic, a sluggish addition of titrant or a distinct indicator may be the answer.
Components Affecting Accuracy
A number of components can affect the accuracy of titration outcomes. These embrace the standard of reagents, the suitability of the indicator, and the presence of interfering substances. Utilizing high-purity reagents and deciding on an applicable indicator that adjustments coloration on the equivalence level are essential for minimizing errors. Contaminants within the pattern or the presence of impurities within the reagents can result in inaccuracies within the calculations.
Minimizing Errors within the Titration Course of
Minimizing errors within the titration course of requires a meticulous method. Cautious approach, constant procedures, and thorough documentation are essential. For example, controlling the speed of titrant addition is significant to make sure a pointy endpoint. This cautious consideration to element is what separates titration from an incredible one.
Suggestions for Exact Measurement and Correct Information Assortment
To make sure the accuracy of your titration outcomes, meticulous consideration to element is crucial.
- Use calibrated glassware for exact quantity measurements.
- Make use of a standardized approach for including titrant.
- Observe the colour change fastidiously and precisely.
- File all observations and measurements meticulously.
- Repeat the titration course of a number of occasions to confirm the outcomes and calculate the common worth.
- Management environmental components, reminiscent of temperature and humidity, to reduce their affect.
- Completely clear glassware to stop contamination and guarantee correct outcomes.
Visible Representations of Titration Curves

Acid-base titrations are like a chemist’s dance, the place you fastidiously add one answer to a different to exactly measure the quantity of 1 substance in one other. The titration curve is the choreographer’s notes, revealing the dance’s steps and the fascinating chemistry occurring through the response. These curves are highly effective instruments for understanding acid-base reactions and figuring out unknown concentrations.Visualizing these reactions by titration curves offers a clearer image of the acid-base chemistry happening.
Every curve, a singular story of proton switch, tells us quite a bit in regards to the nature of the acids and bases concerned. We will analyze the form and options of those curves to find out the equivalence level, a vital landmark within the response.
Sturdy Acid/Sturdy Base Titration
Sturdy acids and powerful bases fully ionize in water. The titration curve of a robust acid titrated with a robust base displays a pointy, vertical rise in pH close to the equivalence level. This sharp change signifies a speedy neutralization of the acid by the bottom. The equivalence level is normally close to pH 7, indicating a impartial answer.
Weak Acid/Sturdy Base Titration
Weak acids, in contrast to their sturdy counterparts, do not totally ionize. The titration curve of a weak acid titrated with a robust base reveals a much less dramatic however nonetheless vital change in pH. The curve has a delicate upward slope in the beginning, adopted by a extra substantial rise in pH across the equivalence level. This mild slope earlier than the equivalence level arises as a result of the weak acid’s conjugate base is a weak base, so the answer resists the pH change.
The equivalence level, sometimes above pH 7, displays the fundamental nature of the ensuing answer.
Weak Base/Sturdy Acid Titration
The titration curve of a weak base with a robust acid is the mirror picture of the weak acid/sturdy base titration. The curve initially has a delicate downward slope earlier than the equivalence level, the place the answer resists the pH change. The sharp change in pH across the equivalence level happens, however the equivalence level is under pH 7, reflecting the acidic nature of the ensuing answer.
Sturdy Base/Sturdy Acid Titration: A Nearer Look
Let’s look at the curve for a robust base titrated with a robust acid. The preliminary pH of the sturdy base answer is excessive, and because the sturdy acid is added, the pH step by step decreases. The graph reveals a steep vertical drop in pH close to the equivalence level. This speedy change signifies the speedy neutralization of the bottom by the acid.
The equivalence level sometimes happens round pH 7.
pH vs. Quantity of Titrant Added
The connection between pH and the quantity of titrant added is key to understanding titration curves. The form of the curve reveals how the pH adjustments because the titrant is added. The steepest a part of the curve close to the equivalence level corresponds to essentially the most speedy change in pH. The curve’s form is intimately related to the character of the acid and base concerned.
This relationship is essential in figuring out the equivalence level and the focus of the unknown answer.
Complete Acid-Base Titration Curve
| Quantity of Titrant (mL) | pH |
|---|---|
| 0 | 13.0 |
| 10 | 12.5 |
| 20 | 11.0 |
| 30 | 10.0 |
| 40 | 9.5 |
| 50 | 9.0 |
| 60 | 8.0 |
| 70 | 7.0 |
| 80 | 6.5 |
| 90 | 6.0 |
| 100 | 5.5 |
This desk offers a hypothetical instance of a robust base titrated with a robust acid. The curve reveals a speedy change in pH across the equivalence level. The desk reveals how the pH adjustments as the quantity of titrant is added, visually representing the titration course of.
